The art of crafting compelling user experience maps is the bread and butter of successful user experience designers. It is common to see product owners craft quick solutions based on an assumption of a user problem or frustration, but experienced designers will advocate for the implementation of some kind of user study into the design process.
The user experience map is exactly as the name suggests: a map that informs us of the user’s needs, feelings, frustrations, and aspirations at each stage of the various touchpoints with our product. Therefore, in order to construct a map of a user, first we need to have some understanding of the user, which is why we need user personas. The user persona is the foundation of user experience research.
Step 1: Crafting a user persona as a prerequisite for a UX map
The purpose of a user persona is to grasp an understanding of the user, such that we are able to produce design research deliverables with credibility. While we’re go into detail on use personas in another post, some of the attributes that we typically include in user personas are as follows:
- Demographics: The most basic data that we compile about the user is their age group, gender distribution, occupation, income, education, and location. This helps us put the other attributes into context
- Goals and motivations: In this attribute, we try to compile the user’s wants, needs, aspirations, and frustrations, which may be relevant to their experience in using our product. This data informs us of key opportunities that we can tap into. It is not uncommon to include user paint points in this section
- Behavioral data: In this attribute, we try to define the user’s habits, values, and personality traits. Including aspects such as lifestyle and personal preferences are the primary ways this data is contextualized
The primary method of collecting data for user personas is user interviews (both qualitative and quantitative), which can be in-person or mass surveying (both paper-based and online).
Researchers can also observe users and conduct focus group studies. It’s a little less common for resource and time-constrained researchers, but these methods can lead to superior results.
Step 2: Defining the scope
Once we have a user persona, we need to decide what kind of experience map we need. This depends on the scope of the project (i.e. is the goal to solve problems holistically, a singular journey within the product, or a singular moment within a singular journey?).
In designing refined experiences, we typically chalk out the different user journeys; for instance, one journey would be the login or signup experience, one journey would be the onboarding experience, and one journey would be accomplishing a user goal within the product. These experiences would then be looked at end-to-end to refine the entirety of the product.
The most common experience maps we create are empathy maps and user journey maps.
The types of experience maps
- User journey map: This is the most common experience map for designing solutions because a user journey map defines all the relevant touchpoints of the product and details the user’s pain points and emotions
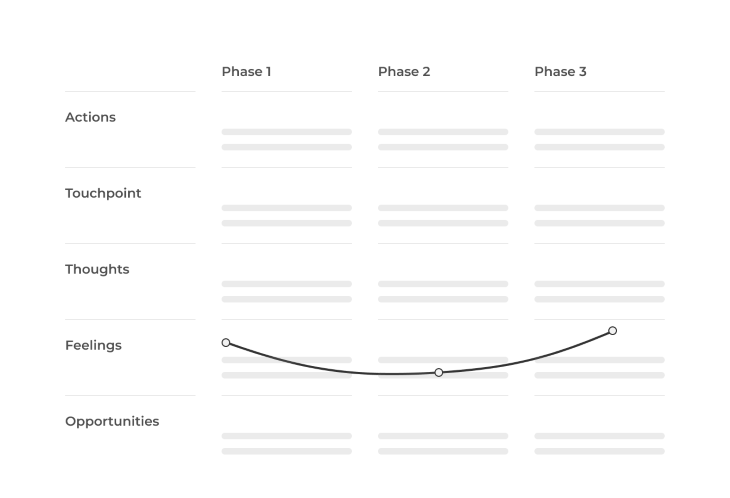
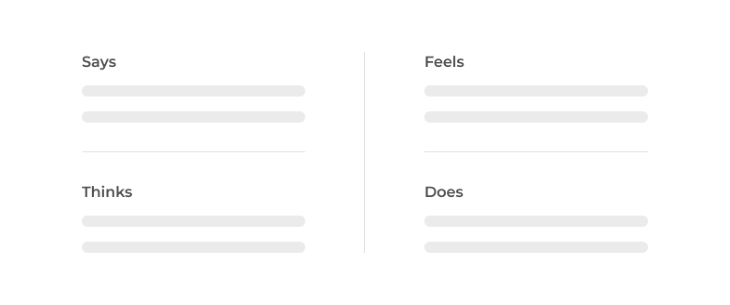
- Empathy map: The empathy map is the next most common experience map. In an empathy map, we detail what a user does, feels, thinks, and says in a tabular format. This helps us visualize the user’s experience
- Service blueprint: This experience map details the user experience and connects it to the mapped-out product service infrastructure that supports the product experience. This map is more complex in nature but is often a necessity for products that achieve scale and have lots of moving parts. The fault lines can be more precisely detected using such an experience map

- Mental model: The mapping of a user’s mental model is essentially detailing the user’s expectations at each step taken to try to accomplish a task. The goal is then to match our product experience to the user’s expectations, such that we can enable the user to accomplish the task with the least friction

There are a couple of other experience maps, context maps and value proposition maps, but the ones detailed above are the most common for designing digital product experiences. We’ll go over these two types briefly.
As noted by O’Reilly Media, context maps outline the interaction between different bounded parts or silos within a product or service. This is used to gain a bird’s eye understanding of the organization, and detect organizational issues.
The value proposition map is used to connect our product’s features and benefits at the various touchpoints to the user’s needs. It is used for purposes such as refining marketing efforts, improving client relationships, and planning the entry of new markets.
A customer journey map is similar to a user journey map, the key difference being that the customer journey map is particularly created with a customer’s interaction with a product or service in mind, whereas a user journey map can have a broader context. Even broader nature is a generic experience map, which doesn’t have anything to do with any product or service but follows the same journey format to understand a person’s experience.
Comparison of the different experience maps
| Empathy map |
|
| Journey map |
|
| Generic experience map |
|
| Service blueprint |
|
| Mental model |
|
| Context map |
|
| Value proposition map |
|
Therefore, whenever proposing new solutions, we are either crafting a journey map or a service blueprint as the final deliverable. Empathy maps, generic experience maps, and mental models are created to help us create better journey maps and service blueprints.
Step 3: Data collection and empathizing with user’s unarticulated needs
The beautiful thing about experience maps is that we have the freedom to be creative. Once we have created user personas and narrowed down our project scope, we now know which experience map format best fits our needs.
We have already discussed user data collection methods such as user interviews, surveys, focus groups, and observation. In recent times, there are several online tools that automate user data collection related to behavior and experience.
Our goal is then to synthesize the hypothesis from this raw data using our educated judgment. It is because we have a detailed understanding of our product that we can define the user’s touchpoints with our product or service.
If not, then we can always perform some user observation. Defining the touchpoints is a crucial step in the data collection process because it is needed in our journey maps and service blueprints.
In every step of the user’s journey, we can then ideate the user’s thoughts, feelings, and pain points based on their goals, motivations, and behavioral data.
For first-time experience map creators, the empathizing process to brainstorm users’ needs might seem tough since we might have to develop theories based on assumptions. Therefore, I recommend to involving users in the experience map creation process. We humans are complex beings and sometimes the findings may be contradictory in nature. Let these contradictions exist and allow any duplicate data to be retained so that you can derive new insights from them.
Here are some questions you can implement to interview users:
- How does the user feel about the existing solution? Does it meet their needs?
- What actions does the user take at every touchpoint to accomplish their goals? How do they discover and interact with these touchpoints?
- What are the user’s feelings?
- Do they face any friction?
- How long does it take them to successfully pass each touchpoint?
Step 4: Creating a robust map with an informed mindset
Regardless of the type of experience map we craft, there are some considerations to guide our mindset such that the contents of the map are truly reflective of our desired outcome. Per the Nielsen Norman Group, the first consideration is to decide whether we are designing for the present or for the future.
If we’re designing for the present, then we just identify the state of affairs today and outline the map based on existing pain point. However, if we are mapping for the future, then we are to propose a future state that we would like our user, product, or service to be in. In such a circumstance, the contents of our map would identify potential future scenarios, pain points, and opportunities.
The next consideration is to identify the level of data we have for creating the map. Do we have detailed user data on the problem we are trying to solve? If there is sufficient data, then we can build a high-fidelity map with concrete, map-centric data. Usually, such data is not readily available; hence, the first version of the map is based on hypothesis. The next iteration of the map can then contain specific, map-centric data based on follow-up user studies.
The third consideration is the level of detail we want to include in our map. Low-fidelity maps are rough overviews of the problem, usually crafted with sticky notes in an unrefined manner. Low-fidelity maps are most commonly used in a collaborative setting. However, high-fidelity maps are the preferred inputs when designing final solutions. High-fidelity maps have detailed user journey data and can have numerous dimensions.
Step 5: Test the hypothesis and refine the map
The first version of a user persona and an experience map is not likely to be fully accurate. However, it’s a starting point. The next step is to either debunk or find proof for the assumptions we made while creating a vibrant and descriptive experience map. In order to find supporting data, we go through the same user study process we went through in the user persona creation process. This time we craft our study with the assumptions in mind and ask follow-up questions to our users.
Once we have gathered new data, we can use it to refine the existing map and make fresh new assumptions based on new findings. The map is then ready for yet another round of refinement, by conducting a user study for our newest assumptions. This iterative process continues, to meet the user’s evolving needs.
The user research process to gather data for our maps can be quite powerful. For instance, instead of just asking the users questions, it may often be helpful to present the users with a prototype to get more tactile information so that we leave less to the user’s imagination and get more accurate answers to our questions. The prototype can be pictures of similar products or concepts or even just a hand-drawn sketch.
Following is an example of a user journey map of availing a ride to the airport.
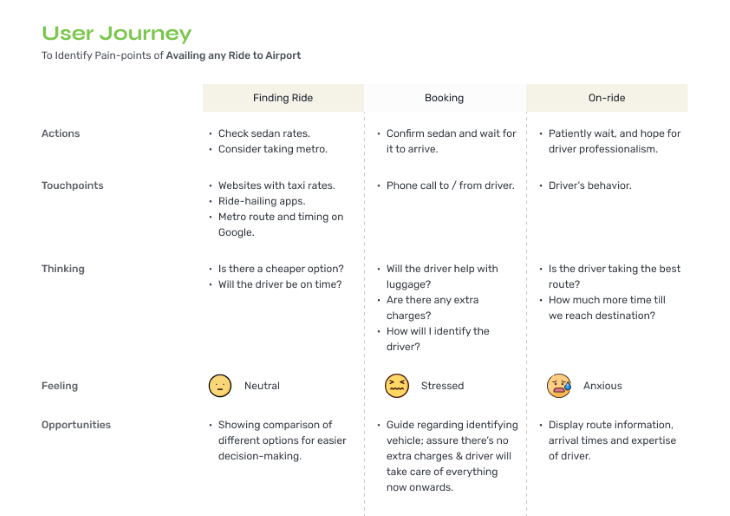
Summary
To create a great user experience map, we have to empathize, be creative, and challenge assumptions. We can gather user data to constantly iterate and refine our maps. If we do this successfully, the map can proudly live as a design artifact, ready for driving design decisions.
Header image source: Flaticon
LogRocket: Analytics that give you UX insights without the need for interviews
LogRocket lets you replay users’ product experiences to visualize struggle, see issues affecting adoption, and combine qualitative and quantitative data so you can create amazing digital experiences.
See how design choices, interactions, and issues affect your users — try LogRocket today.
Source link





Leave a Reply